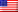
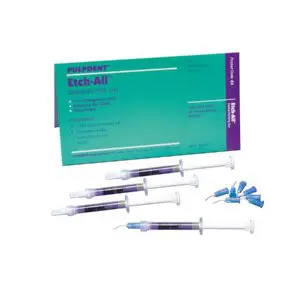
4th Generation Dual Cure System
Description:
Hydrophilic
For bonding to dentin, enamel, porcelain, resins, precious and non-precious metal and amalgam.
The original all-purpose adhesive system
This 4th generation adhesive system offers light cure and self-cure options. The adhesive primer and resin bonding agent are separate components. There is a unique metal primer, and the light cure resin bonding agent Part 1 can also be used to wet plastic instruments to prevent them from sticking to composites.
The patented PMGDM adhesive chemistry with the magnesium salt of NTG-GMA provides higher bond strengths than the earlier PMDM formulas.*
*Bowen RL, inventor. Patent Nos. 4,514,527; 4,521,550; 4,588,756; 4,659,751
*Venz S, Dickens B. Modified surface-active monomers for adhesive bonding to dentin. J Dent Res 1993;73(3):582-86
*Perdigao J, et al. Bons strengths of new simplified dentin-enamel adhesives. Am J Dent 1999;12(6):286-90
Code and Description:
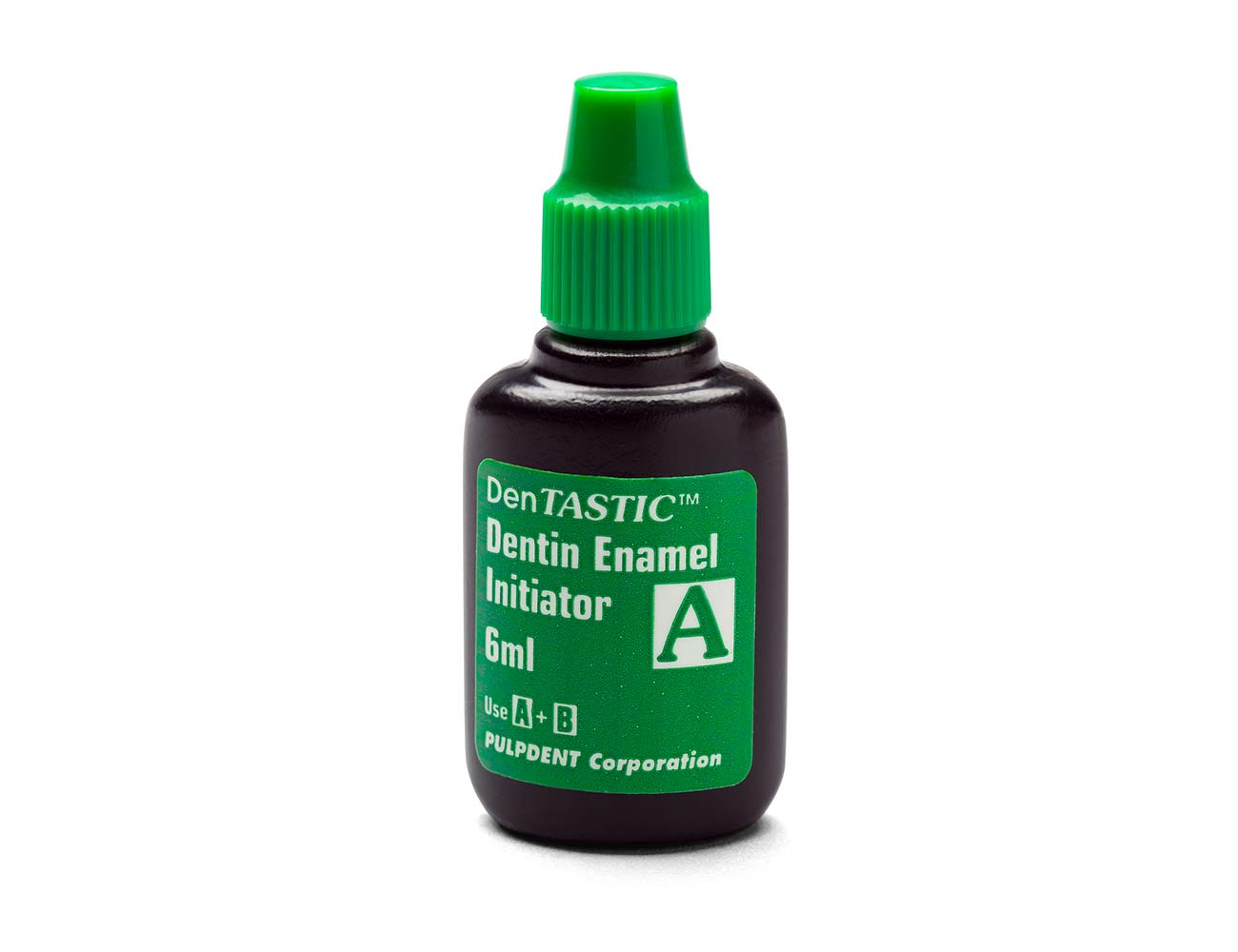

DASP-A – DenTASTIC 6 mL Primer Part A, Dentin/Enamel Initiator
DASP-B – DenTASTIC 6 mL Primer Part B, Universal Base
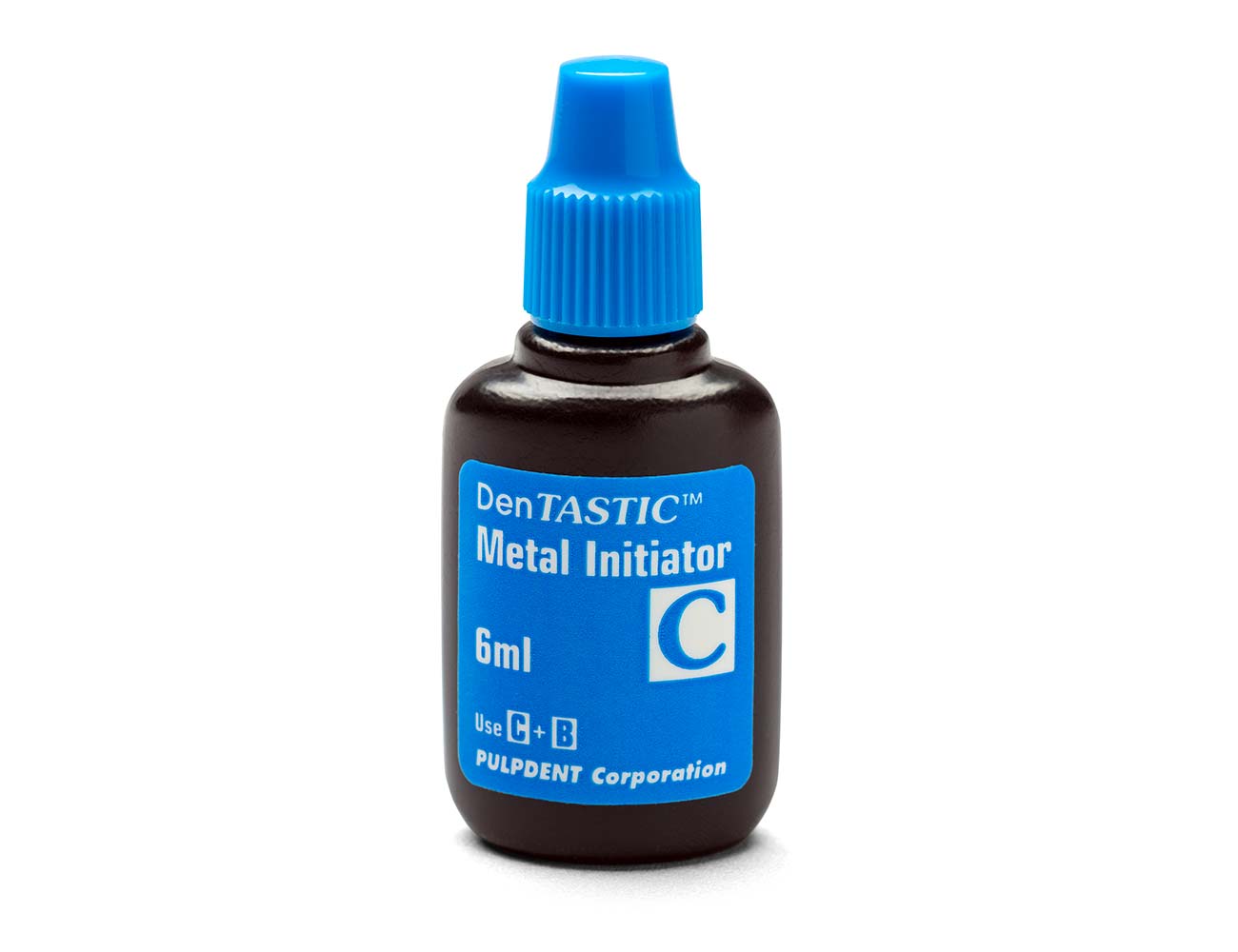

DASP-C – DenTASTIC 6 mL Primer Part C, Metal Initiator

DASP-1 – DenTASTIC 6 mL Unfilled Resin Bonding Agent Part 1, Base, light activated

DASP-2 – DenTASTIC 6 mL Unfilled Resin Bonding Agent Part 2, Catalyst
Order Now:
Sistema de curado dual de 4ª generación
Hidrófilo
Para pegar dentina, esmalte, porcelana, resinas, metales preciosos y no preciosos y amalgamas.
El sistema adhesivo polivalente original
Este sistema adhesivo de 4ª generación ofrece opciones de fotopolimerización y autopolimerización. La imprimación adhesiva y el agente de unión de resina son componentes independientes. Hay una imprimación metálica única, y el agente adhesivo de resina fotopolimerizable Parte 1 también puede utilizarse para humedecer instrumentos de plástico y evitar que se adhieran a los composites.
La química adhesiva patentada PMGDM con la sal de magnesio de NTG-GMA proporciona una mayor fuerza de adhesión que las fórmulas PMDM anteriores.*
*Bowen RL, inventor. Patentes nº 4.514.527; 4.521.550; 4.588.756; 4.659.751
*Venz S, Dickens B. Monómeros tensioactivos modificados para la unión adhesiva a la dentina. J Dent Res 1993;73(3):582-86
*Perdigao J, et al. Bons strengths of new simplified dentin-enamel adhesives. Am J Dent 1999;12(6):286-90
Procedimiento clínico

Reglas básicas:
- Graba o chorrea las superficies, según se indique (estaña las aleaciones de gran valor para obtener mejores resultados).
- Imprime la dentina y el esmalte con la Imprimación Adhesiva DenTASTIC
A + B. - Imprime los metales con la Imprimación Adhesiva DenTASTIC C + B
- Imprimación de porcelana con potenciador de adherencia de silano
- Coloca el Agente Adhesivo de Resina sin Rellenar sobre el DenTASTIC y el Silano (cuando se utiliza un opaquer o cuando se adhiere amalgama nueva, no es necesario el Agente Adhesivo de Resina sin Rellenar).
- Coloca composite restaurador o cemento de resina sobre la resina sin relleno.
Adhesión dentinaria

Anatomía de la dentina
La dentina es un tejido reforzado con fibras formado por minerales, colágeno y agua. El componente mineral es principalmente fosfato de calcio en forma de hidroxiapatita. Al cortar la dentina con una fresa rotatoria se produce una capa de residuos dentinarios.

Tratamiento de superficies
El grabado de la dentina elimina la capa de barrillo dentinario, disuelve los minerales de la superficie exponiendo la matriz de fibras de colágeno y abre ligeramente los túbulos dentinarios. Todos los grabadores de dentina habituales (ácido maleico, nítrico y fosfórico) consiguen los mismos resultados.

Imprimación adhesiva
La Imprimación Adhesiva DenTASTIC A + B forma una matriz entrelazada con el colágeno expuesto y forma tapones en los túbulos dentinarios. Esto se denomina «capa híbrida» y proporciona una extraordinaria retención micromecánica. DenTASTIC® sella permanentemente los túbulos, desensibiliza el diente y protege la pulpa.

Resina sin relleno, composite restaurador y cemento resinoso
El agente adhesivo de resina sin relleno se coloca sobre DenTASTIC para humedecer la superficie adhesiva. Se coloca composite restaurador o cemento de resina sobre la resina sin relleno. Como todas estas resinas y la imprimación adhesiva se basan esencialmente en la misma química, se unen químicamente con una fuerza tremenda y actúan como si fueran una sola.
Interfaz adhesiva de la dentina
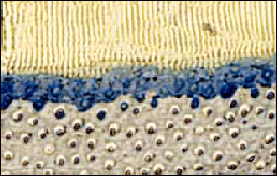
Esta sección de microscopía óptica muestra las tres capas de la interfaz adhesiva dentinaria.
La parte inferior gris muestra la dentina inalterada con los túbulos dentinarios cortados en sección transversal. Las etiquetas adhesivas de resina de imprimación aparecen como pequeños puntos de color azul rojizo en el centro de los túbulos.
La capa híbrida es la banda azul que atraviesa el centro de la diapositiva. Se trata de la matriz entrelazada formada por la imprimación adhesiva, que se tiñe de azul, y las fibras de colágeno de la superficie de dentina desmineralizada.
La capa de color crema de la parte superior es el agente adhesivo de resina sin relleno. Ha reaccionado químicamente con la superficie de la imprimación adhesiva, y esto puede verse en la fina banda azul claro de la parte superior de la capa híbrida azul.
En el sistema de adhesión de 4ª generación, la imprimación adhesiva y el agente adhesivo de resina sin relleno están separados y se aplican en dos pasos distintos.
En el sistema de pegado en un solo paso de 5ª generación, la imprimación adhesiva y la resina sin relleno se combinan en una sola botella.También hay disponible un catalizador de curado dual para este sistema.
Adhesión a porcelana y aleaciones dentales
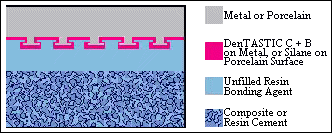
Tratamiento de superficies
El grabado de la porcelana y el arenado o desbastado del metal mejoran mucho la retención micromecánica. Las aleaciones de gran valor deben estañarse con una sencilla técnica de cepillado para obtener resultados superiores.
Imprimación adhesiva
DenTASTIC C + B se adhiere micromecánicamente a las superficies metálicas chorreadas y se adhiere químicamente a los óxidos de las superficies estañadas y de metales no preciosos.Utiliza Silano en Porcelana
Utilizar Silano en Porcelana
Sólo en superficies de porcelana, coloca Silano en lugar de la Imprimación Adhesiva DenTASTIC®. El Silano se adhiere químicamente al sílice de la porcelana y se adhiere químicamente a las resinas restauradoras y al cemento de resina.
Resina sin relleno, composite restaurador y cemento resinoso
El Agente Adhesivo de Resina sin Rellenar humedece la superficie adhesiva, se adhiere químicamente al DenTASTIC y al Silano, y se adhiere micromecánicamente a las superficies grabadas o arenadas. El Agente Adhesivo de Resina sin Rellenar también se adhiere químicamente a las resinas restauradoras y a los cementos de resina. Al fraguar, todas estas resinas actúan como si fueran una sola.
Adhesión con amalgama
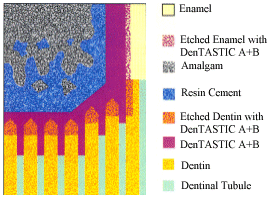
Mediante la tecnología de adhesión de resina, la amalgama se adhiere micromecánicamente a la dentina y el esmalte, eliminando así las microfiltraciones y la sensibilidad postoperatoria.
Graba la dentina y el esmalte, e imprímelos con DenTASTIC A + B. Coloca cemento de resina autopolimerizable o de polimerización dual sobre la superficie adhesiva. Empaqueta la amalgama directamente en el cemento de resina sin curar, forzando a los dos materiales a entremezclarse. Se endurecen juntos en una matriz entrelazada que proporciona una enorme adherencia de la amalgama a la dentina.
Order Now
DenTASTIC® Multiusos
| DASP-A | DenTASTIC 6 ml Primer Parte A, Iniciador Dentina/Enamela |
| DASP-B | DenTASTIC 6 mL Primer Parte B, Base Universal |
| DASP-C | DenTASTIC 6 ml Imprimación Parte C, Iniciador Metálico |
| DASP-1 | Agente adhesivo de resina sin relleno DenTASTIC 6 ml Parte 1, Base, activado por luz |
| DASP-2 | Agente adhesivo de resina sin relleno DenTASTIC 6 ml Parte 2, Catalizador |
Información adicional
| Part | Parte 1, Parte 2, Parte A, Parte B, Parte C |
|---|
Clinical Procedure
Basic Rules

- Etch or sandblast surfaces, as indicated (tin plate high precious alloys for superior results).
- Prime dentin and enamel with DenTASTIC Adhesive Primer
A + B. - Prime metals with DenTASTIC Adhesive Primer C + B
- Prime Porcelain with Silane Bond Enhancer
- Place Unfilled Resin Bonding Agent over DenTASTIC and Silane (when using an opaquer or when bonding new amalgam, Unfilled Resin Bonding Agent is not required).
- Place restorative composite or resin cement over Unfilled Resin.
Dentin Bonding


Dentin Anatomy
Dentin is a fiber reinforced tissue consisting of minerals, collagen and water. The mineral component is mostly calcium phosphate in the form of hydroxyapatite. Cutting dentin with a rotary bur produces a smear layer of dentinal debris.

Surface Treatment
Etching dentin removes the smear layer, dissolves the minerals at the surface exposing the collagen fiber matrix, and slightly opens the dentinal tubules. All the popular dentin etchants (maleic,nitric and phosphoric acid) achieve the same results.

Adhesive Primer
DenTASTIC Adhesive Primer A + B forms an interlocking matrix with the exposed collagen and forms plugs in the dentinal tubules. This is referred to as the “hybrid layer” and provides extraordinary micromechanical retention. DenTASTIC permanently seals the tubules, desensitizes the tooth and protects the pulp.

Unfilled Resin, Restorative Composite & Resin Cement
Unfilled Resin Bonding Agent is placed over DenTASTIC to wet the adhesive surface. Restorative composite or resin cement is placed over the Unfilled Resin. Since all these resins and the adhesive primer are based on essentially the same chemistry, they chemically bond together with tremendous strength and act as though they are one.
Dentin Adhesive Interface

This light microscopy section shows the three layers of dentin adhesive interface.
The gray lower portion shows the unaltered dentin with the dentinal tubules cut in cross section. The adhesive primer resin tags appear as small reddish blue dots in the center of the tubules.
The hybrid layer is the blue band across the center of the slide. This is the interlocking matrix formed by the adhesive primer, which is stained blue, and the collagen fibers in the demineralized dentin surface.
The cream color layer at the top is the unfilled resin bonding agent. It has chemically reacted with the surface of the adhesive primer, and this can be seen in the thin light blue band at the top of the blue hybrid layer.
In the 4th generation bonding system, the adhesive primer and unfilled resin bonding agent are separate and are applied in two separate steps.
In the 5th generation one step bonding system, the adhesive primer and unfilled resin are combined in one bottle.A dual cure catalyst is also available for this system.
Bonding to Porcelain and Dental Alloys

Surface Treatment
Etching porcelain and sandblasting or roughening metal greatly improves micromechanical retention. High precious alloys should be tin plated with a simple brush-on technique for superior results.
Adhesive Primer
DenTASTIC C + B micromechanically bonds to sandblasted metal surfaces and chemically bonds to the oxides on tin plated and non-precious metal surfaces.Use Silane on Porcelain
Use Silane on Porcelain
On porcelain surfaces only, place Silane instead of DenTASTIC Adhesive Primer. Silane chemically bonds to the silica in the porcelain and chemically bonds to restorative resins and resin cement.
Unfilled Resin, Restorative Composite & Resin Cement
Unfilled Resin Bonding Agent wets the adhesive surface, chemically bonds to DenTASTIC and Silane, and micromechanically bonds to the etched or sandblasted surfaces. Unfilled Resin Bonding Agent also chemically bonds to restorative resins and resin cements. Upon setting, all these resins act as though they are one.
Amalgam Bonding

Using resin bonding technology, amalgam is micromechanically bonded to dentin and enamel, thereby eliminating microleakage and post operative sensitivity.
Etch dentin and enamel, then prime with DenTASTIC A + B. Place self-cure or dual cure resin cement on the adhesive surface. Pack amalgam directly into the uncured resin cement, forcing the two materials to intermingle. They harden together in an interlocking matrix which provides tremendous adhesion of amalgam to dentin.
Science & Literature
- The Dental Advisor Jan/Feb 1995;5(1). DenTASTIC ++++.
- CRA Newsletter November 1995;19(11). Bonding Amalgam Update. DenTASTIC.
- RealityNow July 1994, No. 57. DenTASTIC (New).
- Reality 1996;10. Ratings: DenTASTIC.
- Garcia-Godoy F. Shear bond strength for different groups using DENTASTIC. University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, 1995.
- Perdigão J, et al. Bond strengths of new simplified dentin-enamel adhesives. Am J Dent 1999;12(6):286-290.
- Eichmiller F. Biocompatibility data for PMGDM. ADA Health Foundation, Facsimile Transmission. October 30, 1993.
- Van Der Vyver PJ, De Wet FA, Dearlove WR. Shear bond strength of three modern dentine bonding systems. Faculty of Dentistry, University of Pretoria, Pretoria. Abstract.
- CRA Newsletter April 2003;27(4). 10-minute bond strengths of 34 adhesives to 8 buildup resins. DenTASTIC UNO-DUO.
- Bowen RL, Marjenhoff WA. Development of an adhesive bonding system. Operative Dent 1992;Sup 5:75-80.
- Venz S, Dickens B. Modified surface-active monomers for adhesive bonding to dentin. J Dent Res 1993;73(3):582-86.